Kadena command-line reference
The Kadena command-line interface (kadena-cli) provides direct access to the Kadena blockchain and to commands that help you create, test, deploy, and manage applications for the Kadena network.
You can use the Kadena command-line interface to perform tasks interactively or in scripts and automated workflows that don't allow interactive input.
The Kadena CLI has one primary entry point—the kadena parent command.
By providing a single entry point for performing a wide range of tasks, the Kadena CLI integrates naturally into the typical development workflow.
With commands designed specifically for building, testing, and managing Kadena-based applications, you can focus on building innovative applications using familiar tools and processes.
Before you begin
Before you use the Kadena command-line interface, verify the following basic requirements:
-
You have
node, version 18 or later, installed. -
You have the
pnpmpackage manager installed.Depending on your development environment, you can install pnpm using a standalone script or using a package manager. For example, you can run the command
brew install pnpmornpm install --global pnpmto install pnpm on your local computer. For more information about installing pnpm on different operating systems, see Installation.Run
pnpm --versionto verify that you have pnpm installed and the version you are running.
Installation
The Kadena CLI is packaged in a TypeScript library.
You can install the Kadena CLI (@kadena/kadena-cli) using the npm or pnpm package manager.
To install globally using npm, run the following command:
npm install -g @kadena/kadena-clinpm install -g @kadena/kadena-cliTo install globally using pnpm, run the following command:
pnpm install -g @kadena/kadena-clipnpm install -g @kadena/kadena-cliTo verify the package is installed and display usage information, type kadena and press Return:
kadenakadenaCommand overview
You can use the kadena parent command with different flags and subcommands to perform different types of operations.
The basic syntax for running kadena commands is:
kadena <subcommand> <action> [arguments] [flag]kadena <subcommand> <action> [arguments] [flag]The following diagram provides an overview of the kadena command-line interface:
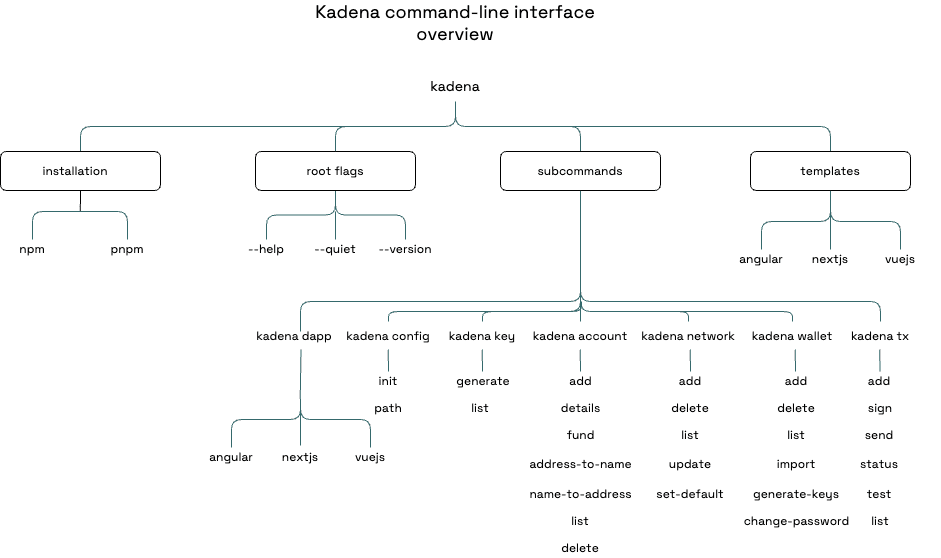
Command subjects
Commands in the Kadena CLI are organized into categories that describe the subject of the action you want to perform. The commands are structured using the following basic format:
kadena <subject> [...<subject>] <action> [--flags] [args]kadena <subject> [...<subject>] <action> [--flags] [args]For example, you can create and manage all wallet-related information by specifying wallet as the command subject.
Available subjects
Use the following command subjects to select the category of information for the operation you want to perform.
| Use this command subject | To do this |
|---|---|
config | Configure the initial context and properties for working with the kadena command-line interface. |
dapp | Create and manage an application project using a frontend framework template. |
wallet | Generate keys and manage wallets. |
key | Generate and manage public and secret keys. |
account | Create, fund, and manage accounts that contain fungibles assets. |
network | Create and manage network information. |
tx | Create and manage transactions. |
help | Display usage information for a specified command. |
version | Display version information. |
Global flags
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| --help | Display usage information. |
| --version | Display version information. |
| --quiet | Eliminate interactive prompts and confirmations. |
| --json | Use JSON format to display relevant result data in standard output (stdout) stream. |
| --yaml | Use YAML format to display relevant result data in standard output (stdout) stream. |
Command-specific help
To get help on a specific subject, use the --help flag:
kadena <subject> --helpkadena <subject> --helpInteractive execution
You can run all commands without any arguments by responding to prompts interactively from the command line. You can skip prompting for any argument by passing your response as part of the command you want to run. Interactive prompting is designed to make command execution more intuitive and easy to follow with a guided user experience.
If you run a command in the Kadena CLI without specifying all of the required options, the CLI automatically prompts you to provide the missing information. This guided approach ensures that you provide all necessary information to successfully execute every command.
To run commands with interactive prompting, type the kadena entry point, the command subject, and the action you want to take without any arguments.
For example, if you want to add a new wallet but aren't sure of all the required flags and arguments, you can run the following command:
kadena wallet addkadena wallet addThe CLI then guides you through the necessary steps, asking for the information required to add the new wallet.
Interactive prompting is especially useful for new users or for users who are less familiar with using command-line tools. It also helps you learn about the arguments required to run different commands, so over time you can reduce or skip interactive prompting by entering arguments directly on the command line.
By allowing you to run commands interactively, the Kadena CLI provides the following key benefits:
- Ease of use: Reduces the need to remember all command arguments and options upfront.
- Guided execution: Ensures that all required inputs are collected before executing a command.
- Flexibility: Allows for a more conversational and less rigid interaction with the CLI.
If you want to disable all interactive prompts and confirmation messages, you can use the --quiet flag.
The --quiet flag enables you to automate tasks in environments where interactive input is impractical, such as continuous integration (CI) pipelines.
If you include the --quiet flag in a command, the command suppresses all interactive prompts and skips confirmations, so that the command executes uninterrupted.
This mode ensures that automated processes can run smoothly and efficiently, without the need for manual intervention.
JSON or YAML output
You can use the --json or --yaml flag to format output from the results of a command in JSON or YAML format.
The results are displayed in the selected format on standard output (stdout).
You can then pipe the output into a file or to other programs.
For example, to format network information using JSON format, you can run the following command:
kadena network list --jsonkadena network list --jsonThe command then displays the results in JSON format:
{ "networks": [ { "network": "devnet", "networkId": "devnet01", "networkHost": "https://localhost:8080", "networkExplorerUrl": "http://localhost:8080/explorer/development/tx/" }, { "network": "mainnet", "networkId": "mainnet01", "networkHost": "https://api.chainweb.com", "networkExplorerUrl": "https://explorer.chainweb.com/mainnet/tx/" }, { "network": "testnet", "networkId": "testnet04", "networkHost": "https://api.testnet.chainweb.com", "networkExplorerUrl": "https://explorer.chainweb.com/testnet/tx/" } ]}{ "networks": [ { "network": "devnet", "networkId": "devnet01", "networkHost": "https://localhost:8080", "networkExplorerUrl": "http://localhost:8080/explorer/development/tx/" }, { "network": "mainnet", "networkId": "mainnet01", "networkHost": "https://api.chainweb.com", "networkExplorerUrl": "https://explorer.chainweb.com/mainnet/tx/" }, { "network": "testnet", "networkId": "testnet04", "networkHost": "https://api.testnet.chainweb.com", "networkExplorerUrl": "https://explorer.chainweb.com/testnet/tx/" } ]}The --json and --yaml options don't affect logging of informational messages, warnings, or errors.
Log messages are sent to standard error (stderr) instead of standard output (stdout).
You can disable the logging of informational messages by setting the KADENA_LOG=output environment variable.
Legacy mode
The --legacy flag ensures that the output format for commands related to wallets, keys, and transactions aligns with earlier cryptographic standards and with existing workflows and tools, such as Chainweaver.
This flag is especially useful if you need to interact with tools that rely on a legacy format for processing transactions or if you need to maintain backwards compatibility for a wallet or other application.
kadena [command] --legacykadena [command] --legacyLegacy mode is available for the following commands:
kadena wallet addkadena key generatekadena tx signkadena wallet addkadena key generatekadena tx sign